Running a Debian virtual machine (VM) on VMware is a fantastic way to experiment with a powerful Linux distribution without altering your main operating system. But to truly unlock its potential, you’ll want to access it remotely from your host machine. This guide will walk you through setting up a seamless remote connection to your Debian VM using SSH from both Windows 11 and Linux hosts.
Why Use a Remote Connection?
Connecting to your VM remotely offers several advantages:
- A Native Experience: Work directly in your host’s terminal or preferred SSH client.
- Easy File Transfers: Securely move files between your host and the Debian VM.
- Automation: Run scripts and manage your Debian environment from your host system.
- Snapshot and Rollback: Before making significant changes, you can take a snapshot of your VM and easily revert if something goes wrong.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, ensure you have the following:
- VMware Workstation or Player installed on your host machine.
- A Debian VM set up and running in VMware.
- Administrative or sudo privileges on your Debian VM.
Step 1: Configure Your Debian VM for Remote Access
First, we need to prepare your Debian VM to accept remote connections.
Install and Enable the SSH Server
- Update Your Package List: It’s always a good practice to start by updating your package lists. Open a terminal in your Debian VM and run:Bash
sudo apt update - Install OpenSSH Server: Next, install the OpenSSH server package, which will allow your VM to listen for incoming SSH connections.Bash
sudo apt install openssh-server - Verify the SSH Service: The SSH service should start automatically after installation. You can verify its status with this command:Bash
sudo systemctl status sshIf the service is not active, you can start it manually:Bashsudo systemctl start ssh
Configure VMware Networking
For your host machine to see your VM on the network, you’ll need to configure the network adapter in VMware. The simplest method for this is using Bridged Mode.
- Shut down your Debian VM.
- In VMware, go to the settings for your Debian VM.
- Select Network Adapter.
- Under “Network connection,” choose Bridged (Connected directly to the physical network). This will make your VM appear as a separate device on your local network.
- Save the settings and restart your VM.
Find Your VM’s IP Address
Once your VM is running with the bridged network adapter, you need to find its IP address. In the Debian terminal, run:
Bash
ip a
Look for the IP address associated with your primary network interface (it will likely be something like eth0 or ens33). It will be listed next to inet. Note this IP address, as you’ll need it to connect from your host.
Step 2: Connecting from Your Host Machine
Now that your Debian VM is ready, let’s connect to it from your Windows 11 or Linux host.
From a Windows 11 Host
Windows 11 comes with a built-in OpenSSH client, making it easy to connect.
- Open PowerShell or Command Prompt.
- Use the following command to connect, replacing
your_debian_usernamewith your username on the Debian VM andyour_vm_ip_addresswith the IP address you found earlier.PowerShellssh your_debian_username@your_vm_ip_address - The first time you connect, you will be asked to verify the authenticity of the host. Type
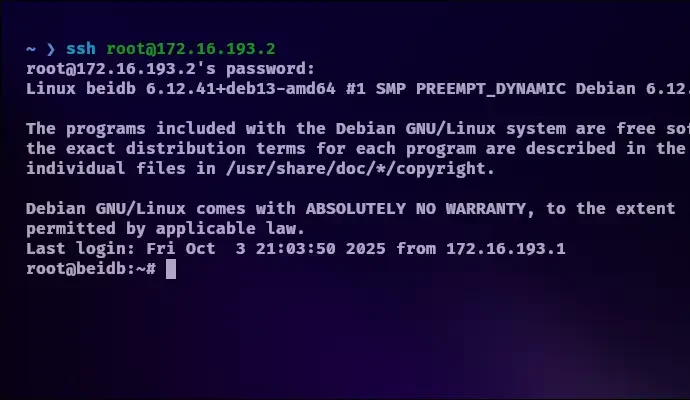
yesand press Enter. - You will then be prompted for your Debian user’s password. Enter it, and you’ll be logged into your Debian VM’s command line!
From a Linux Host
Connecting from a Linux host is very similar.
- Open a terminal.
- Use the
sshcommand, just as you would on Windows:Bashssh your_debian_username@your_vm_ip_address - If it’s your first time connecting, accept the fingerprint by typing
yes. - Enter your password when prompted, and you’re in!
What’s Next?
You now have a fully functional remote connection to your Debian VM! Here are a few things you can do to enhance your experience:
- Set Up SSH Key Authentication: For a more secure and convenient login, consider setting up SSH keys to eliminate the need for a password.
- File Transfers with SCP: Use the
scpcommand to securely copy files and directories between your host and the VM. - Explore Visual Studio Code Remote – SSH: If you’re a developer, the VS Code Remote – SSH extension is a powerful tool for editing files on your VM directly from your host.
By following these steps, you’ve created a more flexible and powerful development and testing environment. Enjoy exploring your Debian VM from the comfort of your host operating system!